关键要点
- 许多 REST 服务中都包含重复的模式;
- 如果能自动生成这些模式相关的代码就可以节省很多时间;
- Visual Studio 的 T4 和 EnvDTE 具有强大的生成代码功能,不需要更多工具辅助;
- 也可以用相似技术生成对 WCF 和数据库的调用;
在 Visual Studio 中,T4 文本模板用文字和控制逻辑的混合物来生成文本文件。控制逻辑是用 Visual C#或者 Visual Basic 语言写成的代码块。在 Visual Studio 2015 Update 2 及以后版本中,也可以在 T4 模板指令中使用 C# V6.0 的新功能。生成的文件可以是任意类型的文本,包括网页、资源文件、甚至是任何编程语言的源代码。在微软公司内部 T4 应用得很广泛。他们用它来生成 MVC 视图、控制器、EntityFramework 上下文等等。
对于那些想要根据已有的模式或模型生成代码,或者写最少的重复性代码的开发者来说,都可以尝试使用 T4。我们可以用 T4 生成代码来简单地封装对业务逻辑或者任何其它服务的调用,也可以增加日志功能、实现缓存机制、基于某些模型来创建请求 / 响应类、甚至实现业务逻辑……等等。
REST 服务通常都被简单地作为业务逻辑的封装器,因此我们就可以使用 T4 来自动地为我们的接口和模型生成 REST/WCF 或者任意其它服务。这样就可以把开发者解放出来,让他们有更多的时间去专心处理用 C#和 SQL 实现的业务逻辑。
用例
假如我们准备开发一个简单的服务,来处理 GET、批量 GET、Insert 和 Update 方法。产品实体包含下面这些属性:
public partial class Product
{
[Key]
public int Id { get; set; }
public string Name { get; set; }
public string Number { get; set; }
public int ProductGroupId { get; set; }
public decimal? ListPrice { get; set; }
public decimal? Size { get; set; }
public decimal? Weight { get; set; }
public ProductGroup ProductGroup { get; set; }
}
需求要求可以通过产品的名字、数量、价格范围等方面来查找过滤产品。当插入一条产品记录时,我们会把除了 Id 和数量之外的所有属性都写上。这些全是自动生成的,所以我们也不能更改它们。为了提高性能,用户也可以指定是否需要添加 ProductGroup 对象。如果不需要联接操作或者隔离 ProductGroup 的查询,就可以不添加。
为了帮助大家理解,我在这里画了一张图来展示我在这篇文章中要用到的架构:
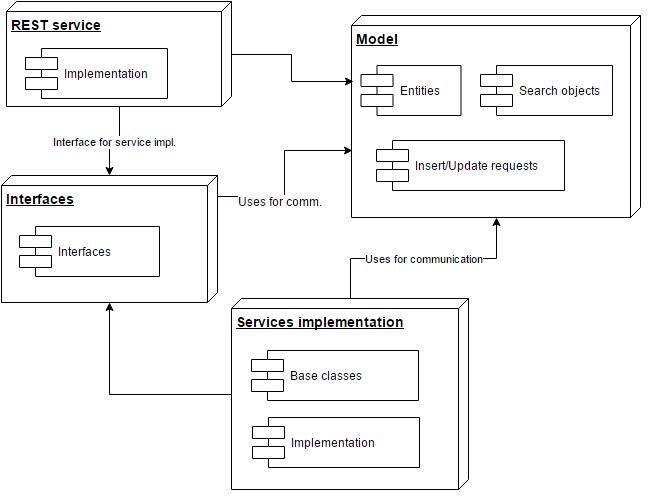
批量 GET 方法
如上文所述,我们需要通过产品的名字、数量或价格范围等做过滤,这通常叫做“过滤类”或者“查询对象”,如果全用手工实现的话就太枯燥了。
但通过 T4、EnvDTE 和模型的属性,我们也可以自动创建新的过滤类。比如,我们可以设置模型的如下属性:
public partial class Product
{
...
[Filter(FilterEnum.GreatherThanOrEqual)]
public string Name { get; set; }
[Filter(FilterEnum.Equal | FilterEnum.List)]
public string Number { get; set; }
[Filter(FilterEnum.GreatherThanOrEqual | FilterEnum.LowerThanOrEqual)]
public decimal? ListPrice { get; set; }
...
}
使用 T4 可以自动生成包含这些属性的类:
public partial class ProductSearchObject : BaseSearchObject<ProductAdditionalSearchRequestData>
{
//some code ommited (private members and attributes)
public virtual System.String NameGTE { get; set; }
public virtual System.String Number { get; set; }
public virtual IList<String> NumberList { get {return mNumberList;} set { mNumberList = value; }}
public virtual System.Nullable<System.Decimal> ListPriceGTE { get; set; }
public virtual System.Nullable<System.Decimal> ListPriceLTE { get; set; }
}
要是使用 EntityFramework 的话,我们就可以轻松生成业务处理逻辑,就是包含基于这个查询对象和模型的 LINQ 查询。要这样做,首先要定义接口和准备使用的属性。比如:
[DefaultServiceBehaviour(DefaultImplementationEnum.EntityFramework, "products")]
public interface IProductService : ICRUDService<Product, ProductSearchObject, ProductAdditionalSearchRequestData, ProductInsertRequest, ProductUpdateRequest>
{
}
做完这一步,T4 就知道了默认的实现应该是怎样,然后就可以生成基于查询对象的检索逻辑了:
protected override void AddFilterFromGeneratedCode(ProductSearchObject search, ref System.Linq.IQueryable<Product> query)
{
//call to partial method
base.AddFilterFromGeneratedCode(search, ref query);
if(!string.IsNullOrWhiteSpace(search.NameGTE))
{
query = query.Where(x => x.Name.StartsWith(search.NameGTE));
}
if(!string.IsNullOrWhiteSpace(search.Number))
{
query = query.Where(x => x.Number == search.Number);
}
if(search.NumberList != null && search.NumberList.Count > 0)
{
query = query.Where(x => search.NumberList.Contains(x.Number));
}
if(search.ListPriceGTE.HasValue)
{
query = query.Where(x => x.ListPrice >= search.ListPriceGTE);
}
if(search.ListPriceLTE.HasValue)
{
query = query.Where(x => x.ListPrice <= search.ListPriceLTE);
}
}
可以把我们的默认实现注册到 IoC 框架中:
public partial class ServicesRegistration : IServicesRegistration
{
public int Priority {get; set; }
public ServicesRegistration()
{
Priority = 0; //This is root, If you want to override this. Add new class with higher priority
}
public void Register(UnityContainer container)
{ container.RegisterType<IProductService,ProductService>(new HierarchicalLifetimeManager());
}
}
如果用这种方法构建,我们还可以非常容易地用另一个更高优先级的类来重载这种注册过程,以此来替换这种实现。
在生成 REST API 时,T4 还会根据接口中的属性信息来决定要为哪些属性生成获取函数。比如,在 IProductService 接口中我们可以为相应属性这样添加函数:
[DefaultMethodBehaviour(BehaviourEnum.Get)]
PagedResult<TEntity> GetPage(TSearchObject search);
既然我们知道了有哪些函数可以用于获取数据,我们就可以为 REST 服务生成代码了:
[RoutePrefix("products")]
public partial class productsController : System.Web.Http.ApiController
{
[Dependency]
public IProductService Service { get; set; }
[Route("")]
[ResponseType(typeof(PagedResult<Product>))]
[HttpGet]
public System.Web.Http.IHttpActionResult GetPage ([FromUri] ProductSearchObject search)
{
//call to partial method
var result = Service.GetPage(search);
return Ok(result);
}
}
如前文所述,我们希望客户端可以按需要请求 ProductGroup 这种附加信息,要具备这个功能,只要给 ProductGroup 属性加上 [LazyLoading] 指令就可以了。
public partial class Product
{
//ommited code
[LazyLoading]
public ProductGroup ProductGroup { get; set; }
}
加上 [LazyLoading] 指令之后,T4 就会给新创建的类中加上 IsProductGroupLoadingEnabled 变量。
public partial class ProductAdditionalSearchRequestData : A.Core.Model.BaseAdditionalSearchRequestData
{
public virtual bool? IsProductGroupLoadingEnabled { get; set; }
}
在底层使用 EntityFramework 会生成如下代码:
protected override void AddInclude(ProductSearchObject search, ref System.Linq.IQueryable<Product> query)
{
if(search.AdditionalData.IsProductGroupLoadingEnabled.HasValue && search.AdditionalData.IsProductGroupLoadingEnabled == true)
{ search.AdditionalData.IncludeList.Add("ProductGroup");
}
base.AddInclude(search, ref query); //calls EF .Include method
}
Insert 方法
插入对象的属性列表常常与完整的模型不同。比如,那些自动生成的主键就不应该由客户端传入,因为它们应该被忽略掉。这个例子当然很明显,但还是有些字段会非常容易出问题。
比如 ProductGroup 属性,如果我们把它也包含到插入对象之中,那大家就会有误解,以为客户端应该用这个函数调用去创建或者更新一个 ProductGroup。所以最好是提供一个明确的插入对象,而不要重用完整模型。
为了避免用重复性地手工劳动来创建这些代码,我们仍然可以用指令来要求它为我们生成需要的属性,比如:
[Entity]
public partial class Product
{
[Key]
public int Id { get; set; }
[Filter(FilterEnum.GreatherThanOrEqual)]
[RequestField("Insert")]
public string Name { get; set; }
[Filter(FilterEnum.Equal | FilterEnum.List)]
public string Number { get; set; }
[RequestField("Insert")]
public int ProductGroupId { get; set; }
[RequestField("Insert")]
[Filter(FilterEnum.GreatherThanOrEqual | FilterEnum.LowerThanOrEqual)]
public decimal? ListPrice { get; set; }
[RequestField("Insert")]
public decimal? Size { get; set; }
[RequestField("Insert")]
public decimal? Weight { get; set; }
[LazyLoading]
public ProductGroup ProductGroup { get; set; }
}
上面的信息可以生成下面的代码,即 ProductInsertRequest 类:
public partial class ProductInsertRequest
{
public System.String Name { get; set; }
public System.Int32 ProductGroupId { get; set; }
public System.Nullable<System.Decimal> ListPrice { get; set; }
public System.Nullable<System.Decimal> Size { get; set; }
public System.Nullable<System.Decimal> Weight { get; set; }
}
和以前一样,我们要修改一下接口,这样 T4 就知道哪些函数是负责处理插入请求的。我们可以为合适的函数加上属性,比如:
[DefaultMethodBehaviour(BehaviourEnum.Insert)]
TEntity Insert(TInsert request, bool saveChanges = true);
有了这些模型和接口的信息,T4 就可以生成我们想要的 REST API 代码了:
[Route("")]
[ResponseType(typeof(Product))]
[HttpPost]
public HttpResponseMessage Insert([FromBody] ProductInsertRequest request)
{
var result = Service.Insert(request);
var response = Request.CreateResponse<Product>(HttpStatusCode.Created, result);
return response;
}
Update 方法
原理也和插入函数一样。在这里我们要为元组的属性加上 [RequestField(“Update”)] 指令,这样就可以为 ProductUpdateRequest 生成合适的属性。然后再为相应的接口加上指令来让 T4 知道哪个函数是要处理 Update 的。
加上这些指令后,T4 就可以为 REST 服务生成更新数据的函数了:
[Route("{id}")]
[ResponseType(typeof(A.Core.Model.Product))]
[HttpPut]
public HttpResponseMessage Update([FromUri] Int32 id, [FromBody]ProductUpdateRequest request)
{
//can return "Not Found" if Update throws NotFoundException
var result = Service.Update(id,request);
var response = Request.CreateResponse<Product>(HttpStatusCode.OK, result);
return response;
}
结论
从文中可以看出,我们可以用 T4 来生成代码,帮助我们节省很多写重复性代码的时间。生成的代码易读性也很好,和自己写的一样。用相同的办法,我们也可以生成代码来在服务级别缓存结果和增加日志功能。
这种技术的另一种用途是同时生成 REST 和 WCF 服务代码,当你的客户端既要支持浏览器也要支持 C#时这就很有用。
在我的工作经历中,我曾经用 T4 和 EnvDTE 来为公司的项目生成完整的 CRUD REST 服务代码,包括数据库调用和单元测试等。几分钟就搞定了,而不是几小时。
如果你想了解更多内容,可以通过 GitHub ,或者直接通过 LinkedIn 联系我。
关于作者
 Amel Musić的职业生涯早年间是为证券公司开发解决方案,主要是银行和政府部门,他的专长是基于 MS SQL Server 和.NET 平台来开发和优化解决方案。在这些系统上做了几年设计之后,他开始学习使用 T4 和面向切面编程,这让他得以减少重复性工作,专心处理客户的业务需求。
Amel Musić的职业生涯早年间是为证券公司开发解决方案,主要是银行和政府部门,他的专长是基于 MS SQL Server 和.NET 平台来开发和优化解决方案。在这些系统上做了几年设计之后,他开始学习使用 T4 和面向切面编程,这让他得以减少重复性工作,专心处理客户的业务需求。
阅读英文原文: Creating RESTful Services with T4 Based on Model and Interfaces




