引言
Hadoop MapReduce 作业有着独一无二的代码架构,这种代码架构拥有特定的模板和结构。这样的架构会给测试驱动开发和单元测试带来一些麻烦。这篇文章是运用 MRUnit,Mockito 和 PowerMock 的真实范例。我会介绍
- 使用 MRUnit 来编写 Hadoop MapReduce 应用程序的 JUnit 测试
- 使用 PowerMock 和 Mockito 模拟静态方法
- 模拟其他类型中的业务逻辑(译注:也就是编写测试驱动模块)
- 查看模拟的业务逻辑是否被调用(译注:测试驱动模块是否运行正常)
- 计数器
- 测试用例与 log4j 的集成
- 异常处理
本文的前提是读者应该已经熟悉 JUnit 4 的使用。
使用 MRUnit 可以把测试桩输入到 mapper 和 / 或 reducer 中,然后在 JUnit 环境中判断是否通过测试。这个过程和任何 JUnit 测试一样,你可以调试你的代码。MRUnit 中的 MapReduce Driver 可以测试一组 Map/Reduce 或者 Combiner。 PipelineMapReduceDriver 可以测试 Map/Reduce 作业工作流。目前,MRUnit 还没有 Partitioner 对应的驱动。MRUnit 使开发人员在面对 Hadoop 特殊的架构的时候也能进行 TDD 和轻量级的单元测试。
实例
下面的例子中,我们会处理一些用来构建地图的路面数据。输入的数据包括线性表面(表示道路)和交叉点(表示十字路口)。Mapper 会处理每条路面数据并把它们写入 HDFS 文件系统,并舍弃诸如十字路口之类的非线性路面数据。我们还会统计并打印所有输入的非路面数据的数量。为了调试方便,我们也会额外打印路面数据的数量。
public class MergeAndSplineMapper extends Mapper<LongWritable, BytesWritable, LongWritable, BytesWritable> {
private static Logger LOG = Logger.getLogger(MergeAndSplineMapper.class);
enum SurfaceCounters {
ROADS, NONLINEARS, UNKNOWN
}
@Override
public void map(LongWritable key, BytesWritable value, Context context) throws IOException, InterruptedException {
// A list of mixed surface types
LinkSurfaceMap lsm = (LinkSurfaceMap) BytesConverter.bytesToObject(value.getBytes());
List<RoadSurface> mixedSurfaces = lsm.toSurfaceList();
for (RoadSurface surface : mixedSurfaces) {
Long surfaceId = surface.getNumericId();
Enums.SurfaceType surfaceType = surface.getSurfaceType();
if ( surfaceType.equals(SurfaceType.INTERSECTION) ) {
// Ignore non-linear surfaces.
context.getCounter(SurfaceCounters.NONLINEARS).increment(1);
continue;
}
else if ( ! surfaceType.equals(SurfaceType.ROAD) ) {
// Ignore anything that wasn’t an INTERSECTION or ROAD, ie any future additions.
context.getCounter(SurfaceCounters.UNKNOWN).increment(1);
continue;
}
PopulatorPreprocessor.processLinearSurface(surface);
// Write out the processed linear surface.
lsm.setSurface(surface);
context.write(new LongWritable(surfaceId), new BytesWritable(BytesConverter.objectToBytes(lsm)));
if (LOG.isDebugEnabled()) {
context.getCounter(SurfaceCounters.ROADS).increment(1);
}
}
}
}
下面是单元测试代码,这段代码中用到了 MRUnit,Mockito 和 PowerMock。
@RunWith(PowerMockRunner.class)
@PrepareForTest(PopulatorPreprocessor.class)
public class MergeAndSplineMapperTest {
private MapDriver<LongWritable, BytesWritable, LongWritable, BytesWritable> mapDriver;
@Before
public void setUp() {
MergeAndSplineMapper mapper = new MergeAndSplineMapper();
mapDriver = new MapDriver<LongWritable, BytesWritable, LongWritable, BytesWritable>();
mapDriver.setMapper(mapper);
}
@Test
public void testMap_INTERSECTION() throws IOException {
LinkSurfaceMap lsm = new LinkSurfaceMap();
RoadSurface rs = new RoadSurface(Enums.RoadType.INTERSECTION);
byte[] lsmBytes = append(lsm, rs);
PowerMockito.mockStatic(PopulatorPreprocessor.class);
mapDriver.withInput(new LongWritable(1234567), new BytesWritable(lsmBytes));
mapDriver.runTest();
Assert.assertEquals("ROADS count incorrect.", 0,
mapDriver.getCounters().findCounter(SurfaceCounters.ROADS).getValue());
Assert.assertEquals("NONLINEARS count incorrect.", 1,
mapDriver.getCounters().findCounter(SurfaceCounters.NONLINEARS).getValue());
Assert.assertEquals("UNKNOWN count incorrect.", 0,
mapDriver.getCounters().findCounter(SurfaceCounters.UNKNOWN).getValue());
PowerMockito.verifyStatic(Mockito.never());
PopulatorPreprocessor.processLinearSurface(rs);
}
@Test
public void testMap_ROAD() throws IOException {
LinkSurfaceMap lsm = new LinkSurfaceMap();
RoadSurface rs = new RoadSurface(Enums.RoadType.ROAD);
byte[] lsmBytes = append(lsm, rs);
// save logging level since we are modifying it.
Level originalLevel = Logger.getRootLogger().getLevel();
Logger.getRootLogger().setLevel(Level.DEBUG);
PowerMockito.mockStatic(PopulatorPreprocessor.class);
mapDriver.withInput(new LongWritable(1234567), new BytesWritable(lsmBytes));
mapDriver.withOutput(new LongWritable(1000000), new BytesWritable(lsmBytes));
mapDriver.runTest();
Assert.assertEquals("ROADS count incorrect.", 1,
mapDriver.getCounters().findCounter(SurfaceCounters.ROADS).getValue());
Assert.assertEquals("NONLINEARS count incorrect.", 0,
mapDriver.getCounters().findCounter(SurfaceCounters.NONLINEARS).getValue());
Assert.assertEquals("UNKNOWN count incorrect.", 0,
mapDriver.getCounters().findCounter(SurfaceCounters.UNKNOWN).getValue());
PowerMockito.verifyStatic(Mockito.times(1));
PopulatorPreprocessor.processLinearSurface(rs);
// set logging level back to it's original state so as not to affect other tests
Logger.getRootLogger().setLevel(originalLevel);
}
}
详解
上面的代码中,我们仅仅检测数据的 ID 和类型,舍弃非路面数据,进行计数,以及处理路面数据。让我们来看一下第一个测试用例。
testMap_INTERSECTION
这个测试用例的预期结果应该是
- SurfaceCounters.NONLINEARS 类型计数器应该自增。
- for 循环应该可以正常工作,即使没有运行到循环体中的 PopulatorPreprocessor.processLinearSurface(surface) 方法。
- 另外两种计数器 SurfaceCounters._ROADS_ 和 SurfaceCounters.UNKNOWN 不会自增。
这是一个 mapper 的测试,所以我们先初始化一个 mapper 的驱动。注意四个类型参数必须与测试目标的类型参数匹配。
private MapDriver<LongWritable, BytesWritable, LongWritable, BytesWritable> mapDriver;
@Before
public void setUp() {
MergeAndSplineMapper mapper = new MergeAndSplineMapper();
mapDriver = new MapDriver<LongWritable, BytesWritable, LongWritable,<br></br> BytesWritable>();
mapDriver.setMapper(mapper);
}
在定义单元测试用例方法的时候使用 IOException
Mapper 可能会抛出 IOException。在 JUnit 中,开发人员可以通过 catch 或 throw 来处理测试目标代码抛出的异常。注意,这里我们并不是专门测试异常情况,所以,我不建议让测试用例方法去捕捉(catch)测试目标代码的异常,而是让测试目标抛出(throw)它们。如果测试目标发生了异常,测试会失败,而这恰恰是我们想要的结果。如果你并非专门测试异常情况,但是却捕捉了测试目标代码的异常,这往往会造成不必要的麻烦。你大可以抛出这些异常并让测试用例失败。
@Test
<b>public void</b> testMap_INTERSECTION() <b>throws</b> <b>IOException</b> {
然后初始化测试桩。为了测试 if-else 块,我们要提供路面类型为 RoadType._INTERSECTION_ 的数据。
LinkSurfaceMap lsm = new LinkSurfaceMap();
RoadSurface rs = new RoadSurface(Enums.RoadType.INTERSECTION);
byte[] lsmBytes = append(lsm, rs);
我们用 PowerMock 来模拟调用类型 PopulatorPreprocessor 的静态方法。PopulatorPreprocessor 是一个拥有业务逻辑的独立的类型。在类级别上,我们用 @RunWith 来初始化 PowerMock。通过 @PrepareForTest,我们告诉 PowerMock 去模拟哪个有静态方法的类型。PowerMock 支持 EasyMock 和 Mockito。这里我们使用 Mockito,所以我们使用了相关类型 PowerMockito。我们通过调用 PowerMockito.mockStatic 来模拟调用静态方法。
@RunWith(PowerMockRunner.class)
@PrepareForTest(PopulatorPreprocessor.class)
PowerMockito.mockStatic(PopulatorPreprocessor.class);
输入之前创建的测试桩并且运行 mapper。
mapDriver.withInput(new LongWritable(1234567), new BytesWritable(lsmBytes));
mapDriver.runTest();
最后,查看结果。SurfaceCounters.NONLINEARS 类型的计数器自增了一次,而 SurfaceCounters.ROADS 类型的计数器和 SurfaceCounters._UNKNOWN_ 类型的计数器没有自增。我们可以用 JUnit 的 assetEquals 方法来检测结果。这个方法的第一个参数是一个 String 类型的可选参数,用来表示断言的错误提示。第二个参数是断言的预期结果,第三个参数是断言的实际结果。assetEquals 方法可以输出非常友好的错误提示,它的格式是“expected:
Assert.assertEquals("ROADS count incorrect.", 0,
mapDriver.getCounters().findCounter(SurfaceCounters.ROADS).getValue());
Assert.assertEquals("NONLINEARS count incorrect.", 1,
mapDriver.getCounters().findCounter(SurfaceCounters.NONLINEARS).getValue());
Assert.assertEquals("UNKNOWN count incorrect.", 0,
mapDriver.getCounters().findCounter(SurfaceCounters.UNKNOWN).getValue());
用下面的语句可以检测 PopulatorPreprocessor.processLinearSurface(surface) 方法没有被调用过。
PowerMockito.verifyStatic(Mockito.never());
PopulatorPreprocessor.processLinearSurface(rs);
testMap_ROAD
这个测试用例的预期结果应该是
- SurfaceCounters. ROADS 类型计数器应该自增。
- PopulatorPreprocessor.processLinearSurface(surface) 方法被调用了。
- 另外两种计数器 SurfaceCounters. NONLINEARS 和 SurfaceCounters.UNKNOWN 不会自增。
测试驱动模块的初始化与第一个用例相似,但有几点不同。
- 初始化一个路面类型的测试桩。 ```
RoadSurface rs = new RoadSurface(Enums.RoadType.ROAD);
2. 设置 log4j 的 debug 级别。 在测试目标代码中,只有 log4j 设置成了 debug 级别,我们才会打印路面数据。为了测试这个功能点,我们先记录当前的 logging 级别,然后我们把根 logger 对象的 logging 级别设置成 debug。
Level originalLevel = Logger.getRootLogger().getLevel();
Logger.getRootLogger().setLevel(Level.DEBUG)
最后,我们把 logging 级别重新设置成原来的级别,这样就不会影响其他测试了。
Logger.getRootLogger().setLevel(originalLevel);
我们看一下测试的结果。SurfaceCounters. _ROADS_ 类型的计数器是自增的。另外两个类型的计数器 SurfaceCounters. _NONLINEARS_ 和 SurfaceCounters._UNKNOWN_ 都不会自增。
Assert.assertEquals(“ROADS count incorrect.”, 1,
mapDriver.getCounters().findCounter(SurfaceCounters.ROADS).getValue());
Assert.assertEquals(“NONLINEARS count incorrect.”, 0,
mapDriver.getCounters().findCounter(SurfaceCounters.NONLINEARS).getValue());
Assert.assertEquals(“UNKNOWN count incorrect.”, 0,
mapDriver.getCounters().findCounter(SurfaceCounters.UNKNOWN).getValue());
使用下面的代码,可以检测出 PopulatorPreprocessor.processLinearSurface(surface) 被调用了一次。
PowerMockito.verifyStatic(Mockito.times(1));
PopulatorPreprocessor.processLinearSurface(rs);
## 测试 Reducer
测试 reducer 和测试 mapper 的原理是相似的。区别在于我们需要创建一个 ReducerDriver,然后把需要测试的 reducer 赋值给这个 ReducerDriver。
private ReduceDriver<LongWritable, BytesWritable, LongWritable, BytesWritable>
reduceDriver;
@Before
public void setUp() {
MyReducer reducer = new MyReducer ();
reduceDriver = new ReduceDriver <LongWritable, BytesWritable,
LongWritable, BytesWritable>();
reduceDriver.setReducer(reducer);
}
## 配置 MAVEN POM
如果使用 JUnit 4,那么还要在 Maven 的 POM.xml 配置文件中添加下面的配置项。可以在 PowerMock 的官方网站上找到 Mockito 相关的版本信息。
在 Eclipse 中运行
这个单元测试可以像其他 JUnit 测试一样运行。下面是在 Eclipse 中运行测试的示例。
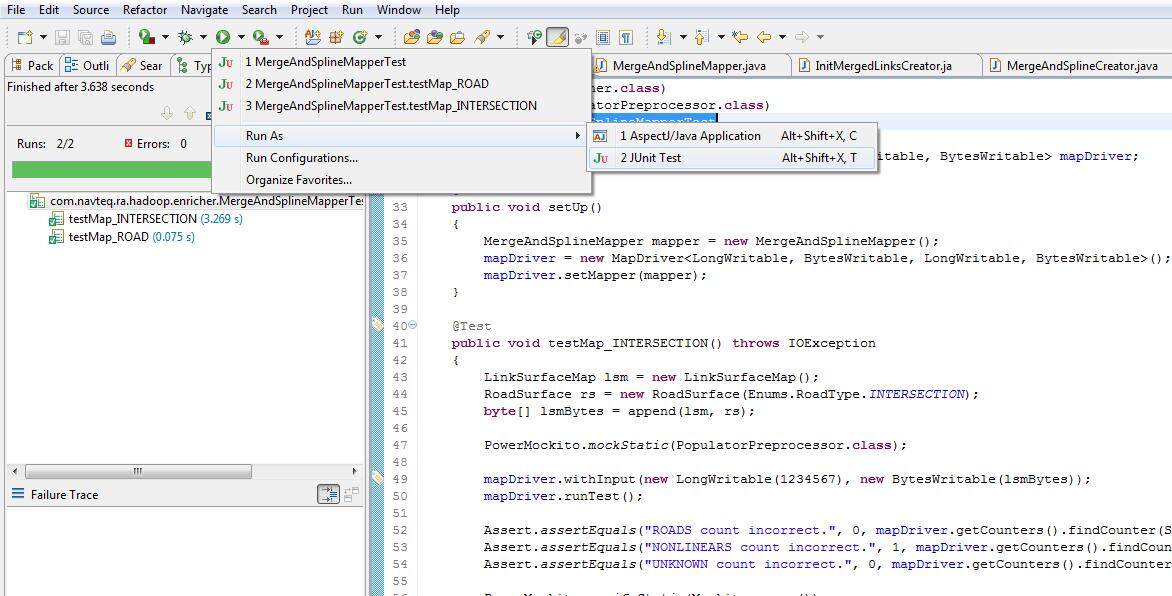
结论
MRUnit 是一种轻量但非常强大的测试驱动开发的工具。它可以帮助开发人员提高代码测试覆盖率。
感谢
我要感谢 Boris Lublinsky 帮助我完成了项目。还要感谢 Miao Li 为项目添加了许多 MRUnit 测试用例。
查看英文原文: Unit Testing Hadoop MapReduce Jobs With MRUnit, Mockito, & PowerMock
感谢杨赛对本文的审校。
给InfoQ 中文站投稿或者参与内容翻译工作,请邮件至 editors@cn.infoq.com 。也欢迎大家通过新浪微博( @InfoQ )或者腾讯微博( @InfoQ )关注我们,并与我们的编辑和其他读者朋友交流。




